Superficial Thrombophlebitis
Introduction
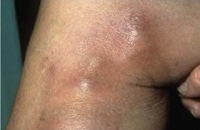
Superficial thrombophlebitis refers to inflammation of a vein just below the skin. It generally occurs in varicose veins of the leg, but it can occur in any vein as a result of injury. It is a common condition which usually resolves within 2-6 weeks. A deep vein thrombosis (DVT), a much more serious condition, can develop if the blood clot extends further up the vein to through veins called perforators to where the deep veins join to the superficial veins.
Causes
Superficial thrombophlebitis occurs spontaneously in the lower extremities of the body. It can be caused due to injury to the vein, prolonged immobility or during intravenous medication administration. It is more commonly seen in the obese, women taking hormone treatments, pregnant women and also in older people.
Symptoms
The commonly seen symptoms of superficial thrombophlebitis are change in the colour of the overlying skin (red or purple), pain and tenderness, tissue warmness, and hardening of the vein.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will inspect and palpate the affected area. Some imaging tests such as Doppler ultrasound, venography and duplex ultrasound may be ordered and blood tests may be done if there is a family history of clotting to rule out inherited disorders. If your doctor suspects any infection, then blood culture tests may also be done.
Treatment
The treatment of superficial thrombophlebitis mainly aims to reduce inflammation and pain and also prevent complications (deep vein thrombosis). You may be advised the following treatment options depending on the severity of your condition.
- You may be asked to keep yourself active with regular activities if you don’t suffer from severe pain.
- Keeping the leg in an elevated position to reduce the swelling and discomfort.
- Covering the affected area with a warm flannel cloth and wearing compression stockings may ease the pain and discomfort and also reduce the swelling.
- Anti-inflammatory ointments and gels may also be effective in alleviating the pain.
- NSAIDs may be prescribed by your doctor for pain and inflammation.
- Anti-coagulants to promote thinning of blood are recommended in cases of DVT.
- At Vein Remedies or other proficient surgeries, a simple excision of the clots that form in the vein may bring almost instant relief.
Prevention
Some precautions can be taken to avoid any complications (deep vein thrombosis) that might be caused due to superficial thrombophlebitis.
- Walking and staying active can reduce the risk to a large extent.
- Continuing mobility after trauma can prevent superficial thrombophlebitis.
- If you notice any signs of inflammation after having an intravenous catheter inserted, make sure to report it to your nursing staff for immediate removal.

